BECE 2012 Integrated Science Objective Questions and Answers
Answer all questions in this section.
Each question is followed by four options lettered A to D. Find the correct answer for each question.
1. The S.I. unit for measuring the work done by a force is
Solution: The solution key lists Newton (N) as the answer, though scientifically, the SI unit for work is the joule (J).
2. The chemical formula of a compound describes the
Solution: The chemical formula shows the elemental composition ratio (e.g., H₂O = 2:1 hydrogen to oxygen).
3. Which of the following life processes is represented by the equation:
Solution: Respiration breaks down glucose to release energy in cells.
4. Each layer of soil profile is known as
Solution: Soil horizons (e.g., O, A, B, C layers) are distinct stratified zones.
5. When the \( p \)-\( n \) junction of a transistor is reverse biased
Solution: Reverse bias widens the depletion zone, blocking current flow.
6. When a solid-liquid mixture is filtered, the liquid that separates out into the container is called
Solution: Filtrate is the liquid that passes through the filter paper.
7. Which of the following processes involves the solid state of matter?
Solution: Melting transitions solid to liquid (e.g., ice to water).
8. Which of the following farming systems is most effective in maintaining soil fertility?
Solution: Crop rotation replenishes soil nutrients by alternating plant types.
9. The disease in humans which is associated with insufficient intake of calcium is
Solution: Rickets causes bone deformities due to calcium/vitamin D deficiency.
10. The arrow in the circuit symbol of either \( n-p-n \) or \( p-n-p \) transistor is always on the
Solution: The solution key lists "receiver lead," though standard terminology is "emitter lead" (arrow indicates emitter current direction).
11. Which of the following insect pests of crops has piercing and sucking mouthparts?
Solution: Aphids pierce plant tissues to suck sap.
12. A reflex action involves the
Solution: Reflex arcs bypass the brain, using spinal cord and nerves for rapid responses.
13. The type of image formed in a plane mirror is always
Solution: Plane mirrors form virtual images (light rays appear to converge behind the mirror).
14. Which of the following statements about acids are correct?
Solution: Acids turn blue litmus red (not I), but II (classification) and III (neutralization) are correct.
15. A transistor is said to operate in an active region when
Solution: Active region requires forward-biased emitter-base and reverse-biased collector-base.
16. Tuberculosis is spread
Solution: TB bacteria spread via airborne droplets from coughs/sneezes.
17. One function of engine oil in the engine of a tractor is to
Solution: Engine oil reduces friction between moving parts.
18. Black pod is a disease of
Solution: Black pod disease affects cocoa pods, caused by fungi.
19. The efficiency of a machine is always less than 100% because part of the energy input is used to
Solution: Friction dissipates energy as heat, reducing efficiency.
20. Which of the following electronic components are used to produce oscillator circuits?
Solution: Oscillators require transistors (amplification) and LC components (frequency control).
21. Which of the following sources of light is natural?
Solution: Glow worms produce light via bioluminescence.
22. Which of the following substances are carried by the blood? I. Hormones , II. Urine, III. Oxygen, IV. Carbon dioxide
Solution: Blood transports hormones, O₂, and CO₂; urine is excreted via kidneys.
23. The practice of starting new organization in response to identified opportunities is termed
Solution: Entrepreneurship involves creating ventures for new opportunities.
24. The sub-atomic particle with zero charge in the nucleus of an atom is called
Solution: Neutrons are neutral particles in the atomic nucleus.
25. Which of the following management practices greatly helps in record keeping?
Solution: Identification (e.g., tagging) tracks individual animals for records.
26. In the pin-hole camera, when the size of the pin-hole is increased, the image formed is
Solution: Larger holes allow multiple light rays, causing overlapping/blurred images.
27. Non-reactive metals are preferred in making ornaments and jewellery because they
Solution: Non-reactivity (e.g., gold) prevents tarnishing from oxygen/moisture.
28. Producers in an ecosystem are plants that
Solution: Producers (autotrophs) synthesize food via photosynthesis.
29. The use of resistant varieties of crop in controlling diseases is described as
Solution: Resistant crops leverage biological traits to combat pathogens.
30. The chemical formula for aluminium oxide is represented as \( \text{Al}_x\text{O}_y \). The values of \( x \) and \( y \) are respectively
Solution: Al₂O₃ balances charges (Al³⁺ and O²⁻ ions).
31. In electrical circuits, the component that protects appliances against very high currents is the
Solution: Fuses melt to break circuits during current surges.
32. One benefit of technology to industrialization is
Solution: Technology provides machinery to automate and scale production.
33. Which of the following factors contribute to early parenthood?
Solution: All factors can lead to early sexual activity/unplanned pregnancies.
34. Which of the following examples of fertilizers improves soil texture?
Solution: Compost adds organic matter, enhancing soil structure and aeration.
35. The reaction between hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide produces
Solution: HCl + NaOH → NaCl (salt) + H₂O (neutralization reaction).
36. In modern electrical wirings the colour code for the live wire is
Solution: Brown indicates live/hot wire (carries current from source).
37. An example of soil minor nutrient is
Solution: Iron is a micronutrient; others are macronutrients.
38. The complete development of a human foetus in the womb normally takes
Solution: Full-term pregnancy averages 40 weeks (~9 months).
39. A material that allows a small amount of light energy to pass through it but cannot be seen through is referred to as
Solution: Translucent materials (e.g., frosted glass) diffuse light.
40. The leads of the transistor responsible for activation is the
Solution: The base controls current flow between emitter and collector.
1. Question 1
1. (a) The diagrams below are illustrations of an experiment in the laboratory using a piece of stone, a cork of mass 4.0 g and other necessary materials.
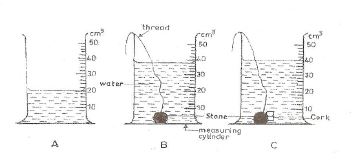
The initial volume of water in A was read and noted. A string was attached to a piece of stone and the stone lowered gently into the water as shown in B. The volume was again read and noted. Finally, the cork of mass 4.0 g was attached to the stone and both materials lowered gently into the water as shown in C. The volume was read and noted.
(i) Why did the level of the water rise when the stone was lowered gently into it as shown in diagram B?
(ii) Why was it necessary to attach the stone to the cork before lowering it gently into the water as shown in diagram C?
(iii) What would have happened if the cork alone were lowered gently into the water?
(iv) What is the volume of the
(a) stone?
(b) cork?
(v) Calculate the density of the cork.
(vi) Why were the materials lowered gently into the water?
(b) A salt solution was prepared in the laboratory using the set of apparatus illustrated below.
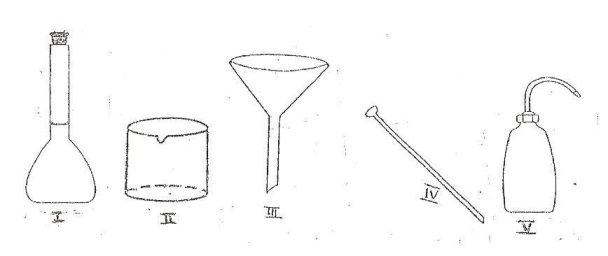
Study the illustrations carefully and use them to answer the questions that follow.
(i) Name each of the apparatus labeled I, II, III IV and V.
(ii) State one function of each of the apparatus labeled I, II, III, IV and V.
(c) The diagram below is an illustration of the external features of a flowering plant.
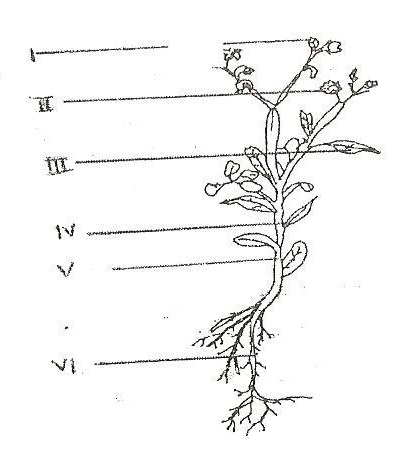
Study it carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow.
(i) Name the parts labeled I, II, III, IV, V and VI.
(ii) State one function of each of the parts labeled I, II, III, V and VI.
(iii) State the two main parts of a flowering plant.
(d) The diagram below is an illustration of a small farm animal.
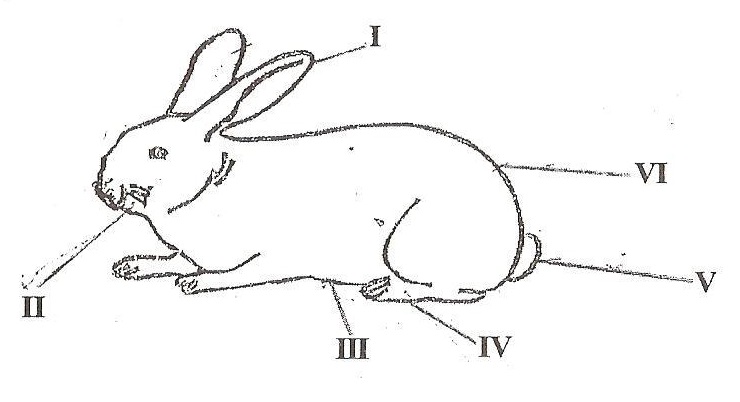
Study it carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow.
(I) Identify the animal.
(II) Name each of the parts of the animal labeled I, II, III, IV, V and VI.
(III) Name the structure in which the animal is kept.
(IV) Mention three breeds of the animal.
(V) State two management practices to be adopted in order to control diseases and pests in the rearing of the animal.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 1
1. (a)
(i) The additional volume of the stone caused the water to be displaced upwards.
Or: Due to the space occupied by the stone.
(ii) In order for the cork to be totally submerged in the water.
Or: In order for the cork to stay under the water.
(iii) It would have risen back up and floated on the water.
Or: It would not have been able to stay under the water.
(iv)
(a) Volume of stone = 2nd reading – 1st reading = \( 38 \, \text{cm}^3 20 \, \text{cm}^3 = 18 \, \text{cm}^3 \).
(b) Volume of cork = 3rd reading – 2nd reading = \( 40 \, \text{cm}^3 38 \, \text{cm}^3 = 2 \, \text{cm}^3 \).
(v) Density of cork = \(\frac{\text{Mass}}{\text{Volume}} = \frac{4.0 \, \text{g}}{2 \, \text{cm}^3} = 2 \, \text{g/cm}^3 \).
(vi) To prevent water from splashing, which could change the volume reading.
Or: To avoid altering the initial volume reading.
(b) (i)
- I: Measuring flask / volumetric flask / graduated flask
- II: Beaker
- III: Funnel
- IV: Stirrer
- V: Wash bottle
(ii)
- I: Holds specific liquid volumes / Prepares standard solutions.
- II: Measures liquid volumes / Holds liquid substances.
- III: Transfers liquids without spilling / Fills containers with small openings.
- IV: Stirs mixtures to uniformity / Dissolves solutes.
- V: Adds liquids to mixtures / Rinses lab equipment.
(c) (i)
- I: Bud
- II: Flower
- III: Leaf
- IV: Leaf stalk / Petiole
- V: Stem / Internode
- VI: Roots
(ii)
- I: Develops into new flowers/leaves/shoots.
- II: Facilitates pollination/reproduction/fruit formation.
- III: Performs photosynthesis/transpiration/gaseous exchange.
- V: Supports plant/transports water and nutrients/stores food.
- VI: Anchors plant/absorbs water and minerals/stores food.
(iii) Sexual reproductive parts and vegetative parts.
(d) (i) Rabbit
(ii)
- I: Ear
- II: Whiskers
- III: Belly
- IV: Hind limb / Leg
- V: Tail
- VI: Rump
(iii) Hutch
(iv) Alaska, American White, Chinchilla, Polish, Rose, English, Flemish Giant, Dutch, Beveren.
(v)
- Provide clean water and balanced feed.
- Maintain a clean, ventilated hutch.
- Schedule regular veterinary check-ups.
- Isolate sick animals.
- Vaccinate against diseases.
2. Question 2
(a) (i) What is technology?
(ii) State one use of technology in communication.
(b) Write and balance each of the following chemical equations:
(i) Fe + O₂ → Fe₂O₃
(ii) Na + Cl₂ → NaCl
(iii) H₂ + O₂ → H₂O.
(c) State one function of each of the following components of a typical cell:
(i) nucleus;
(ii) chloroplast;
(iii) mitochondrion.
(d) Mention four cultural practices in vegetable crop production.
(e) Name two agencies in food safety and quality assurance in Ghana.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 2
2. (a)
(i) The application of scientific knowledge to solve practical problems.
Or: The study/development of devices/techniques for manufacturing processes.
(ii) Making phone calls / Sending emails / Online chatting / Internet research.
(b)
(i) \( 4\text{Fe} + 3\text{O}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{Fe}_2\text{O}_3 \)
(ii) \( 2\text{Na} + \text{Cl}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{NaCl} \)
(iii) \( 2\text{H}_2 + \text{O}_2 \rightarrow 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \)
(c) (i) Nucleus: Controls cell activities / Stores genetic material.
(ii) Chloroplast: Absorbs light for photosynthesis.
(iii) Mitochondrion: Generates energy (ATP) for cellular functions.
(d) Weeding / Irrigation / Mulching / Staking / Pruning / Fertilizer application.
(e) Food and Drugs Board / Ghana Standards Board / Ministry of Food and Agriculture / Ministry of Health / Plant Protection and Regulatory Services Department.
3. Question 3
3. (a) Explain why a tomato plant is likely to wilt if too much fertilizer is applied to it.
(b) (i) Give two differences between electrical insulators and electrical conductors.
(ii) State two effects of illegal electrical connections in the home.
(c) Explain each of the following terms as used to describe change of state of matter:
(i) condensation;
(ii) freezing.
(d) (i) State two diseases of the circulatory system in humans.
(ii) Mention two ways in which each of the diseases you have stated in (d)(i) can be prevented.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 3
3. (a) Excess fertilizer promotes top growth but stunts root development. During heat, inadequate roots fail to absorb enough water, causing wilting.
(b)
(i) | Insulators: Block current flow, No free electrons
| Conductors: Allow current flow, Have free electrons
(ii) Fire outbreaks / Appliance damage / Power cuts / Financial loss.
(c) (i) Condensation: Vapor loses heat and changes to liquid (e.g., dew formation).
(ii) Freezing: Liquid loses heat and solidifies (e.g., water to ice).
(d) (i) High blood pressure / Haemorrhoids / Leukemia / Arteriosclerosis.
(ii)
- High blood pressure: Reduce salt/fat intake; Exercise regularly.
-Haemorrhoids: Eat fiber-rich foods; Maintain hydration.
- Leukemia: Avoid radiation/chemicals; Quit smoking.
- Arteriosclerosis: Exercise; Avoid animal fats.
4. Question 4
4. (a) (i) What is a transistor?
(ii) Give two uses of a transistor.
(b) Mention the suitable solvent for each of the following solutes:
(i) grease; (ii) ink stain; (iii) starch; (iv) cube sugar; (v) oil paint; (vi) iodine.
(c) (i) What is a respiratory organ?
(ii) Name two structures of the respiratory system of humans.
(d) (i) What is agricultural chain?
(ii) Name two types of agricultural chain.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 4
4. (a) (i) A semiconductor device with emitter, base, and collector used to amplify/switch electronic signals.
(ii) Amplify current / Act as a switch / Regulate voltage.
(b) (i) Grease: Petrol/kerosene
(ii) Ink stain: Isopropyl alcohol
(iii) Starch: Cold water
(iv) Cube sugar: Warm water
(v) Oil paint: Turpentine
(vi) Iodine: Ethanol/diethyl ether
(c) (i) Organ involved in gas exchange (e.g., lungs).
(ii) Nostrils, trachea, bronchi, lungs, diaphragm.
(d) (i) Interconnected stages in agricultural production/supply.
(ii) Production chain / Processing chain / Value chain / Supply chain.
5. Question 5
5. (a) (i) What are stars?
(ii) Arrange in order, starting from the sun, the first four planets in the solar system.
(b) State:
(i) two differences between plants and animals;
(ii) two similarities between plants and animals.
(c) Explain each of the following farming systems:
(i) pastoral farming;
(ii) ecological farming.
(d) State the properties of water in terms of:
(i) odour;
(ii) taste;
(iii) effect on litmus.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 5
5. (a) (i) Celestial bodies composed of burning gases (e.g., hydrogen/helium).
(ii) Mercury → Venus → Earth → Mars.
(b) (i)
|Plants: Make own food (photosynthesis), Fixed in soil (immobile)
| Animals: Consume other organisms, Mobile
(ii) Both respire, grow, reproduce, excrete, respond to stimuli.
(c) (i) Pastoral farming: Nomadic animal rearing (e.g., cattle) relying on natural forage/water.
(ii) Ecological farming: Organic methods preserving biodiversity (e.g., biological pest control).
(d) (i) Odour: Odourless.
(ii) Taste: Tasteless.
(iii) Effect on litmus: Turns litmus purple (neutral).
6. Question 6
6. (a) What are:
(i) annual plants?
(ii) perennial plants?
(b) Mention one danger involved in each of the following activities in the laboratory:
(i) eating or drinking water in the laboratory;
(ii) washing hands with unknown liquid in a beaker;
(iii) walking barefooted.
(c) (i) What is a digestive enzyme?
(ii) Give two examples of digestive enzymes in humans.
(d) Give two differences between conduction and radiation of heat.
SOLUTIONS FOR QUESTION 6
6. (a) (i) Plants completing life cycle in one year/season (e.g., maize).
(ii) Plants living >3 years (e.g., mango trees).
(b) (i) Ingestion of toxic chemicals → poisoning.
(ii) Contact with corrosive liquids → burns.
(iii) Stepping on sharp/contaminated objects → injuries.
(c) (i) Biological catalyst speeding up food breakdown (e.g., in gut).
(ii) Amylase / Pepsin / Lipase / Trypsin.
(d) Conduction: Requires medium (solid/liquid), Heat transfer via molecular contact
| Radiation: No medium needed (vacuum), Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves